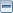
Hermit Thrush, Catharus guttatus
The Hermit Thrush is primarily a migrant and winter visitor to Tennessee arriving in early October and departing by late April. It is the only brown thrush you'd expect to see in the state during the winter months.
The Hermit Thrush is a quiet, unobtrusive bird spending most of its time foraging in the leaf litter or in berry-filled tangles at the forest edge . A behavioral characteristic that makes this bird easier to identify is its habitat of flicking its wings when perched and quickly raising and slowly lowering its ruddy-colored tail.
While a Hermit Thrush nest has yet to be found in Tennessee, males have been heard singing and juvenile birds have been found on Roan Mountain for the past 10 years. The breeding range for this species extends across the boreal forest south through the western and northeastern United States and only recently has the breeding range extended into the southern Appalachians. Hermit Thrush winter over much of the Southeast and south through Mexico to El Salvador.
Description: This medium-sized thrush has a brown back and reddish tail. It has black spots on a white chest, buffy sides of the chest, a thin whitish eye-ring, and a bill that is pale at the base and black at the tip. The Hermit Thrush cocks its tail up and flicks its wings frequently.
It also characteristically lifts its tails up quickly and lowers it slowly. Both male and female look alike. While often difficult to see, its distinct chup or tuck call note, sometimes repeatedly given from a low perch, may reveal its presence.
Length: 6.75"
Wingspan: 11.5"
Weight: 1.1 oz
Voice: The song is a melodious flute-like warble, mostly on one pitch, starting with a clear whistled single note. The call, commonly heard in winter, is a low chup or tuck.
Similar Species:
Swainson's Thrushes are similar, but have a very distinct buffy eye-ring and a strong buffy wash on the breast. The tail is the same color as the back, and is not reddish.
Gray-cheeked Thrushes have only a partial eye-ring and the tail does not contrast as sharply with the back.
The Hermit Thrush is the only brown thrush expected in Tennessee during the winter.
Habitat: The Hermit Thrush winters in moist forests with a dense understory, open woodlands, and especially in ravines and sheltered sites. It breeds in the interior of deciduous, mixed, and coniferous forest. In the Appalachians, it breeds in the high-elevation spruce-fir forest.
Diet: Insects and other arthropods, including fruit in winter.
Nesting and reproduction: The first breeding season record of an adult Hermit Thrush in Tennessee was in 1966 on Roan Mountain. As of the spring of 2009, no nests have been found.
Clutch Size: Usually 3 to 4 eggs with a range of 2 to 5 eggs.
Incubation: The female incubates the eggs for 11 to 13 days.
Fledging: Both parents feed the young, and the chicks fledge in 11 to 12 days.
Nest: Built by the female, the nest a bulky cup of grasses, leaves, mosses, twigs, rootlets, hair, mud, and lichens, and lined with finer material. It is placed on or near the ground, or low in small trees.

 Author
Topic: BIRDS OF TENNESSEE 2021 to 2025 (Read 133924 times)
Author
Topic: BIRDS OF TENNESSEE 2021 to 2025 (Read 133924 times)